Until the late 1970s to early 1980s blow molding machines were primarily delivered with contractor control. This type of control offered the advantage that the electrical components could be checked by appropriately trained maintenance personnel and easily replaced in the event of a fault. Changes in the machine control system could be made with the help of simple auxiliary devices. However, the disadvantages were the susceptibility to faults and short service life due to wear of mechanically moving parts, the large number of components (up to 150 contactors, 12 temperature controllers, etc.), the size of the components, and how these elements were connected. This type of control was called “hard-wired programmed logic controller”.
Blog
RADIAL WALL THICKNESS DISTRIBUTION IN BLOW MOULDING
In blow moulding, the wall thickness distribution of the finished article is essentially determined by the wall thickness distribution of the parison, its position in relation to the blow mould cavities, and the local stretching paths.
On the one hand, falling below a given wall thickness specification leads to defective articles. On the other hand, an oversupply of material in other areas causes unnecessary costs and also has a negative effect on the cooling time and thus on the cycle time.
To achieve the goal of efficient production with maximum output at minimum material and energy consumption, standard axial wall thickness control is not sufficient for articles with complex geometries.
The optimization of the radial (partial) wall thickness distribution of a blow moulded hollow part not only increases the economic efficiency of the production process, but also enables a sustainable blow moulding process with a significant reduction in CO2 emissions by reducing the amount of material used and the energy required per article produced (reduction of the required plasticizing and cooling capacity).
Special wall thickness control system for influencing the radial wall thickness distribution over the circumference of the parison are described in the following sections.
There are currently 2 major system being used in the process,
- SFDR – Statically Flexible Deformable Ring
- PWDS – Partial wall thickness distribution system
The details of both the system will be shared in the next blog.
Statically Flexible Deformable Ring (SFDR®)
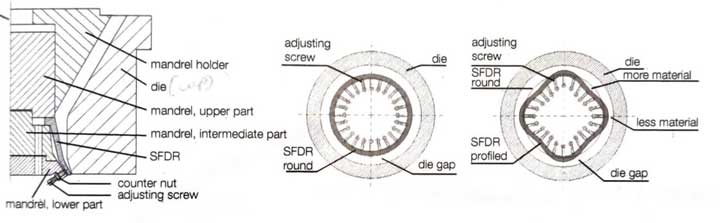
While the standard (axial) wall thickness control WDS = Wall-thickness Distribution System), as described in Section 2.3.5, is sufficient for simple rotationally symmetrical articles such as round bottles, articles with a rectangular cross-section (e.g. rectangular bottles or jerry cans) or with complex geometry are expected to have thin spots in the area of large stretch ratios, such as in the area of corners, shoulders, or edges. The thinnest point over the circumference determines the die gap to be set to meet the wall thickness specification and thus the material used for this cross-section. However, since the material supply is constant over the cross-section when using axial wall thickness control, thick spots appear on the article in the areas of low stretching. Here, in a first step, machining (profiling) of the die can help. This leads to an influence on the wall thickness distribution over the circumference of the parison, which is effective over the entire length of the parison. For each optimization step, the die must be removed again and again and the die ring or core pin must be machined until the optimum profile is achieved. When using the “statically flexible deformable ring” (SFDR®) as part of the mandrel, for a likewise defined radial influence on the parison wall thickness, the mandrel is profiled by deforming a flexible ring using adjusting screws. The advantage of the SFDR is that the profiling can be adapted t the requirements without dismantling the mandrel simply by adjusting the screws. This allows for quick optimization of the article without the risk of overshooting the mark. To optimize a product change with regard to set-up time and reproducibility, SFDR systems with exchangeable inserts are state-of-the-art nowadays. The exchangeable inserts can be changed within the few minutes and allow the SFDR profile to be adapted to the new product without having to remove the mandrel tool or adjust the adjusting screws.
Partial Wall Thickness Distribution System (PWDS®)
The radial die gap and thus the parison wall thickness over the circumference is the PWDS® system. Preferably in combination with the static profiling of an SFDR, the PWDS allows variable (dynamic) adjustment of the wall thickness distribution over the parison length. A “dynamically flexible deformable ring” (DFDR) is deformed by two servo-hydraulically or electrically driven actuators by pushing and/or pulling during parison ejection according to the specification of one or more profile curves. For each wall thickness point of the profile curve, the radial die gap is partially adjusted over the circumference. In combination with the standard wall thickness control, the PWDS system allows optimum adjustment of the parison wall thickness both over the circumference and in the axial direction.
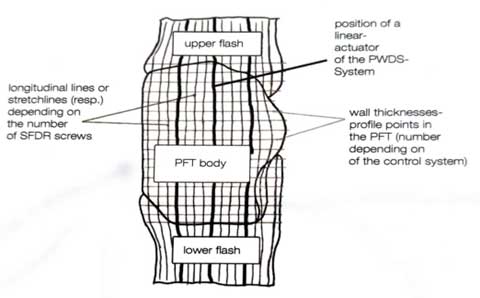
Below figure shows a schematic illustration of the principle course of the profile points of the wall thickness control and the longitudinal or stretching lines corresponding to the adjusting screws of the SFDR in the case of a PFT.
Blogs
CLAMPING UNITS IN EXTRUSION BLOW MOULDING
In all extrusion blow molding processes, a blow mold consisting of two halves closes around the parison once it has reached its full length. These two halves of the mold are mounted on the so-called mold mounting platens, which from part of the clamping unit (or closing unit).
SWELLING BEHAVIOUR OF THE PARISON
The visco – elastic behavior of the thermoplastics (here the memory effects) in conjunction with the flow channel geometry in the head causes the diameter of the parison to change after leaving the die. The wall thickness also changes and thus the length of the parison. This phenomenon is called ‘; die swell’’.
MANDREL HEADS IN EBM
In mandrel heads (also referred to as ‘’heart – shaped – curve heads’’, or cardio did heads) the solid core part is massively integrated into the basic structure of the head. These heads are also called side-fed heads.
SPIDER HEADS IN EBM
The main task of parison heads (blow heads or even just heads) is to divert the compact melt flow as supplied by the extruder into a vertical downwards flow movement and to form melt tube with a uniform circumferential wall thickness distribution.
EXTRUDER WITH GROOVED FEED ZONE
Blow moulding machines with grooved barrel extruders are universal machines for all types of polyolefin; the grooved barrel system is,however, indispensable for high molecular weight, high viscosity raw materials. In these extruders, the cylinder wall in the feed section features tapered longitudinal grooves.
SMOOTH BORE EXTRUDER
Blow molding machines with smooth – bore extruders are more or less limited to the processing of low to medium molecular weight polyolefin types. Smooth bore extruders are less expensive than those with a grooved feed zone and show less screw wear.
Is a Blow Molding Machine Used to Make Anything Other than Plastic Bottles?
For manufacturing plastic bottles, experts rely on a state-of-the-art blow molding machine. With this particular process, a manufacturer produces a broad range of finished products in varying sizes and shapes. Because of that, multiple industries depend on a professional company to make a specific type of plastic bottle needed.
What Are the Future Trends of Plastic Molding Machines?
Although the plastic molding industry took a hit this year due to the instability within the automotive industry, it’s still on target for breaking records. After all, the plastic molding machine is something that a broad range of industries rely on for both internal operations and the making of consumer goods. As demand increases, you can expect to see some exciting changes for plastic molding machines.
Can Extrusion Blow Molding Produce Complicated Shapes
When it comes to extrusion blow molding capability, most people think of standard plastic bottles, tight-head containers, jars, and larger water containers. However, the extrusion blow molding process can do much more. In fact, when using a technologically advanced extrusion blow molding machine, it can produce finished products with complicated shapes, and in varying sizes.
Rotational Molding: Advantages and Disadvantages
Rotational moulding offers a number of benefits, but it’s not the best production process for every part. So how do you decide if it’s a fit for you? Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of the process is the first step toward making a decision with confidence.
Importance of Extrusion Blow Moulding Machine in the Pharma Industry
Nowadays plastic is the reliable and most effective form of packaging for different industries and pharmaceutical domains. In the pharmaceutical sector, two types of polymers are used, thermoplastics and thermosets.
HOW TO START A TOY-MAKING BUSINESS WITH EBM IN INDIA?
Before starting the toys making business, it is important to do market research. It is important to collect as much information as possible about this business so that you get the knowledge of exactly what kind of toys are in demand in the market.
WHY INDIAN GOVT. ENCOURAGES TOY MAKING BUSINESSES MAKING BUSINESS
Indian government motivates and urges the Indian startups in the toy sector to maximize manufacturing and increase the reach of Indian made toys to the world. After holding a meeting with senior officials and ministers, the Prime Minister make a statement and urge the start-ups and young blood to innovate in the toy sector. Also, PM has given the suggestion to the educational institutions to arrange competitions in toy technology and design.
Biodegradable vs. Recyclable Plastics
Biodegradable plastics undergo digestion by microbes to form natural bi-products and what is known as humus (a sludge that makes an excellent plant fertiliser). It also produces gas which is officially known as biogas. Biozone’s landfill-biodegradable plastics have proprietary additives that help them biodegrade naturally in landfills. Once the biodegradable packing ends up in a landfill, it attracts the necessary microbes that break down the plastic into its natural components.
The Future of the Extrusion Blow Molding Machine
Everywhere you look, competition among different industries has exploded. Thanks to a thriving market, companies that once struggled now see incredible success. Just as businesses need ways to stay ahead of the competition, so do extrusion blow moulding machine manufacturers. Because of that, they continually push to come up with more innovative solutions.
Why CMP Machines are the BEST?
Innovation is at the heart of any successful company. Innovation keeps an organization at the top of their game, allowing them to flex their competitive muscles and take pride in the work they do.
What is Multilayer Extrusion Blow Moulding Machine?
Nowadays literally all humankind use plastic products 24/7 all over the world. It is super easy to get access to all kinds of plastic products. You might have come across bottles that have a shiny layer on the outer side, or different colours on the outer and a different one in the inner. So, what it is? It is a multilayer extrusion product. Well, let me explain to you how what it is exactly.
Exterior Surface (Mold Cavity) Design
The inner and outer walls of the part are formed simultaneously and integrally, but interior and exterior designs are essentially independent so we review them separately. As the design develops, the designer should begin thinking about the interaction of the plastic and the mould that will produce the part. The visual exterior of many products is formed in one half of the mould called a cavity. Following are some of the features of mould cavities the designer will want to consider.
Interior Surface (Mold Core) Design
The inner and outer walls of the part are formed simultaneously and integrally, but interior and exterior designs are essentially independent so we review them separately. As the design develops, the designer should begin thinking about the interaction of the plastic and the mould that will produce the part. The interior surface of double-wall blow moulded parts is normally formed by a mould core. Since the mould core must fit inside the cavity, there should be no question it meets the same core blow ratio = W>2D overall size requirement as the cavity.
About Parison and Parison Control
Parison blow moulding of intricate plastic bottles and other plastic parts requires air pressure control that is precise, repeatable and rapid responding. Proportion-Air offers electronic closed-loop pressure and flow control used to improve processes in the plastics blow moulding industry.
Why CMP Blow Moulding Machine?
Multiple industries and outside manufacturing companies depend on advanced extrusion blow moulding machinery. Without the right machine, there would be no way to produce superior quality products and we, at CMP, provide quality over quantity. Let us go through the advantages you will get for using CMP’s machine.
Information about the series of Extrusion Blow Moulding Machines in CMP
Have you ever seen a person at the fair or the mall during the holidays, blowing glass to create beautiful, artistic designs? It’s mesmerizing how a random piece of coloured glass can be manipulated by precisely placed hot air and become such a masterpiece. This art form inspired the current method of manipulating plastics to form many of the items we use every day, from water bottles to toys and so many things in between. This artful method is called Extrusion Blow Molding and it’s a common and inventive way of mass-producing hollow, lightweight products that are also durable and waterproof
How to select a Blow Moulding Machine?
The reputation of the blow moulding machine manufacturer you do business with has a lot to do with the quality of the equipment it sells. The right company takes great pride in offering its customers top-of-the-line products at a competitive price. Buying a blow moulding machine can be a nerve-racking experience for fresh entrepreneurs.
Types of products manufactured in Extrusion Blow Moulding Machine
Blow moulding is a manufacturing process for forming and joining together hollow plastic parts. In general, there are three main types of blow moulding: extrusion blow moulding, injection blow moulding (one stage), and injection stretch blow moulding (two stages). In the extrusion blow moulding process (EBM), plastic is melted and extruded into a hollow tube (a plastic parison). This plastic parison is then captured by closing it into a cooled metal mould. Air is then blown into the parison, inflating it into the shape of the hollow bottle, container, or part. After the plastic has cooled sufficiently, the mould is opened and the part is ejected. It is designed to manufacture high volume hollow plastic products.
Types of material used in Extrusion Blow Moulding Machine
When choosing a material for blow moulding; cost, density, flexibility, strength, and other factors should be considered into what resin is best for your part. If the elastomeric properties of the material are exceeded, a hole will tear through the material resulting in a defective part. Other relevant properties are largely based on your application and might include mechanical, physical, chemical resistance, heat, electrical, flammability or UV resistance.
Extrusion Blow Moulding Machine VS Injection Blow Moulding Machine
If you operate a business that requires specially formed plastic bottles or containers, such as juice and water bottles or liquid soaps and shampoos, it’s to your benefit to understand the various manufacturing processes for making those bottles and containers.
What are the 2 types of Extrusion Blow Moulding Machines?
Blow moulding is a manufacturing process used for the production of plastic bottles, containers, and custom shapes. At Central Machinery and Plastic Products, we use extrusion blow moulding (EBM). EBM bottles are easily identifiable by their pinch line across the base of the bottle. This line is created as the mould cavity closes on the parison and the tail is trimmed off.
The process of Extrusion Blow Moulding Machine
Extrusion Blow Molding is the simplest type of blow moulding. A hot tube of plastic material, called a parison, is dropped from an extruder and captured in a water-cooled mould. Once the moulds are closed, the air blown through the top of the neck of the container. When the hot plastic material is blown up and touches the walls of the mould, the material freezes, the container now maintains its rigid shape.
What is Extrusion Blow Moulding Machine?
Blow moulding is an umbrella term for forming hollow plastic parts by inflating a molten plastic tube or parison until it fills a mould and forms the desired shape. Think of it as inflating a balloon inside of a water bottle. The blow moulding process begins with melting down the plastic and forming it into a parison. The parison is a tube-like piece of plastic with a hole in one end through which compressed air can pass. Water channels are carved into the mould to assist in cooling.
